One universal truth that everyone can agree on is; building a house or a construction project requires many different materials and quite a lot of them. The sheer scale of a project along with the other various aspect such as the cost, time, effort, and emotional factors makes every construction a mega project, and why not? For most of us, we build a house once in our life turn it into a home, and pass it on to the next generation. However, a lack of appropriate construction materials with proper planning can hamper the building and create a continuous problem for a long time.
Due to its position in the Himalayas and its susceptibility to natural catastrophes like earthquakes, Nepal has had several difficulties concerning housing and infrastructure. The nation needs robust and sustainable housing materials, as the terrible earthquake of 2015 made clear. Here we will discuss how to build a house in Nepal using different materials.
Understanding the Local Context
Before beginning the building process, it is critical to understand the local environment, which includes the topographical, climatic, and socioeconomic elements that impact housing in Nepal. Because of the country’s unique geography, which ranges from the high mountains to the low-lying Terai plains, different construction techniques and materials are required to meet the distinct demands of each location.
Mountain Region:
This region, with its steep hills and difficult weather conditions, necessitates the adoption of materials that can survive high temperatures and heavy snowfall. Stone and wood are widely utilized in this location because they provide insulation and are easily available.
Hills:
Temperatures and rainfall are mild in Nepal’s hilly area. Houses in this region are frequently constructed from locally accessible materials such as stone, mud, and lumber. To prevent landslides and soil erosion, the sloping terrain needs the installation of retaining walls and suitable drainage systems.
Terai Region:
The Terai region is suitable for agriculture due to its flat topography and fertile soil. Mud, bricks, and bamboo are commonly used to construct houses in this region. However, during the monsoon season, the region is prone to floods, necessitating the building of higher foundations and suitable drainage systems.
Earthquake-Resistant Design Principles
Creating a solid foundation:
A well-designed foundation is critical for a house’s stability during an earthquake. Cement footings and reinforced concrete foundations are recommended for increased earthquake resilience.
Making use of slip layers:
To increase earthquake resilience, slip layers of wood or concrete can be kept between layers of brick and mud walls. These layers aid in the distribution of stresses generated by an earthquake, lowering the likelihood of wall collapse.
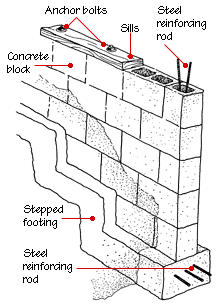
Corner and wall reinforcement:
Walls can be strengthened with rebar or other strong materials to increase their strength and stability during an earthquake. This is especially critical for multi-story structures, which should be built using cement or cement blocks reinforced with rebar.
Appropriate Building Materials
Selecting appropriate building materials is crucial for constructing resilient and sustainable houses in Nepal. Some suitable materials include:
TMT Rebars: Compared to other iron and steel bars used for construction, TMT rebars are far stronger, ductile, and long-lasting. Thermo-mechanically treated (TMT) steel rebar is essential for providing ductility in reinforced concrete constructions. TMT rebars are heated and cooled in a specific procedure that alters their molecular structure, making the steel more ductile. This means that TMT rebars may bend and deform more before breaking than standard mild steel bars.
TMT rebars of higher-grade equal TMT rebar of an enhanced grade. One such premium TMT bar that provides the ideal balance of flexibility and toughness is Rhino 500D TMT Rebars. Rhino 500D Rebar is the first and the only steel TMT rebar in grade Fe 500D with superior ductility introduced in Nepal. It also marks the beginning of the New Industry Quality Benchmark for Steel Rebars in Nepal. With superior ductility and earthquake resistance properties, Rhino 500D compared to other normal grade rebars is highly suitable for applications in areas and regions highly prone to seismic risks like Nepal.
Another option from Jagdamba Steels is Jagdamba E Steel Rebar. Jagdamba E is a Fe 500 Grade Earthquake Resistant Steel Rebar. It is the first and only of its kind of superior Steel Rebar available in Nepal and is specially made for applications in earthquake-resistant constructions. Since Nepal is highly prone to seismic risks, the application of Jagdamba E Steel Rebar can help minimize the risks like damage to the RCC structures and thereby help save lives in case of an Earthquake due to its resistant features.
Stone and Mud: Traditional Nepali buildings are frequently made using stone and mud, which are both widely available and inexpensive. These materials can be coupled with slip layers and strengthened with rebar or other strong materials to increase earthquake resistance.
Corrugated Metal Roofing: Lightweight corrugated metal roofing is recommended for earthquake-resistant houses, as it is less likely to cause injury or damage during an earthquake compared to heavier materials like slate. For metal roofing, using a Galvalume metal roof like Jagdamba Supershine Jasta Pata can ensure longevity and superb protection. The sheets are manufactured through advanced Galvalume line technology with electrolytic cleaning, NOF (Non-Ox) Furnace, in-line tension leveling equipment, and skin pass mill process. These sheets are not just eye-appealing, they are also safe to install and highly durable. Due to its durability, and low maintenance, Jagdamba Super Shine is preferred for diverse purposes from commercial buildings to residents.
Community Involvement and Skill Development
Involving local people in the development process is critical to the long-term viability and sustainability of Nepali housing projects. Hiring a local contractor that is conversant with local construction laws and regulations is vital. A local contractor can also assist you in deciding on the best materials and building procedures for your home. Furthermore, they can assist you in navigating the local bureaucracy and obtaining the necessary permits for house construction.
It is crucial to consider the local culture. For instance, most homes in the region have a traditional design, with a large veranda or porch. Additionally, it is common to have a separate cooking area, called a “chulo.” By incorporating local cultural elements into your house, you can make it more attractive and appealing to the local community.
Building resilient and sustainable housing in Nepal necessitates a thorough understanding of the local environment, the application of earthquake-resistant design concepts, the use of appropriate building materials, and active community participation. By following these recommendations, you may build residences that not only endure natural calamities but also contribute to your, your family’s, and your home’s long-term well-being.
